题目
链接:622. 设计循环队列
难度:Medium
设计你的循环队列实现。 循环队列是一种线性数据结构,其操作表现基于 FIFO(先进先出)原则并且队尾被连接在队首之后以形成一个循环。它也被称为“环形缓冲器”。
循环队列的一个好处是我们可以利用这个队列之前用过的空间。在一个普通队列里,一旦一个队列满了,我们就不能插入下一个元素,即使在队列前面仍有空间。但是使用循环队列,我们能使用这些空间去存储新的值。
你的实现应该支持如下操作:
- MyCircularQueue(k): 构造器,设置队列长度为 k 。
- Front: 从队首获取元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
- Rear: 获取队尾元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
- enQueue(value): 向循环队列插入一个元素。如果成功插入则返回真。
- deQueue(): 从循环队列中删除一个元素。如果成功删除则返回真。
- isEmpty(): 检查循环队列是否为空。
- isFull(): 检查循环队列是否已满。
示例:
MyCircularQueue circularQueue = new MycircularQueue(3); // 设置长度为 3
circularQueue.enQueue(1); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(2); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(3); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(4); // 返回 false,队列已满
circularQueue.Rear(); // 返回 3
circularQueue.isFull(); // 返回 true
circularQueue.deQueue(); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(4); // 返回 true
circularQueue.Rear(); // 返回 4
题解
循环队列
这道题比较朴实,就是实现一个循环队列,相信对任何一个学过数据结构的人来说都没什么问题,这里用一张动图来简单演示一下。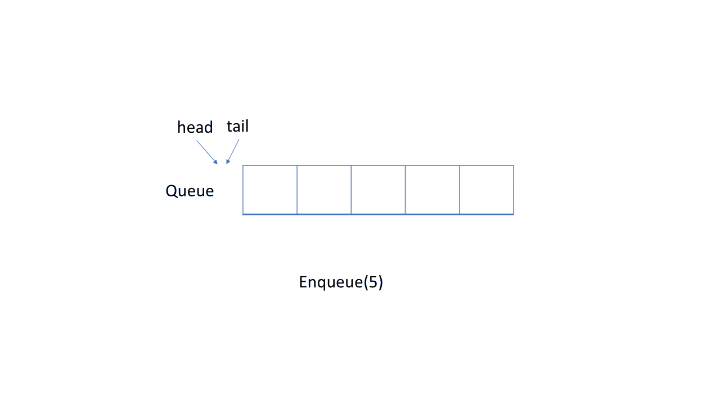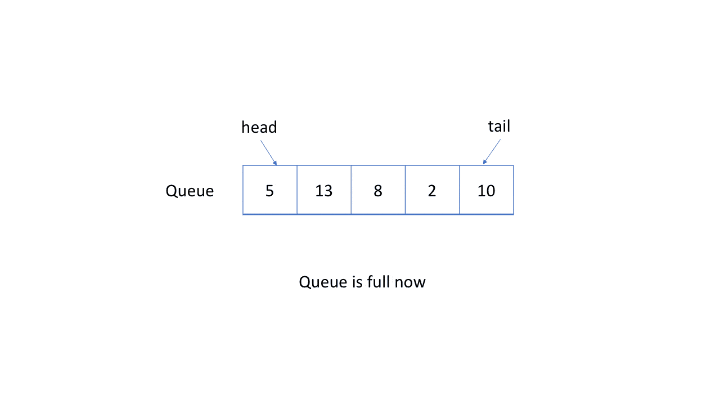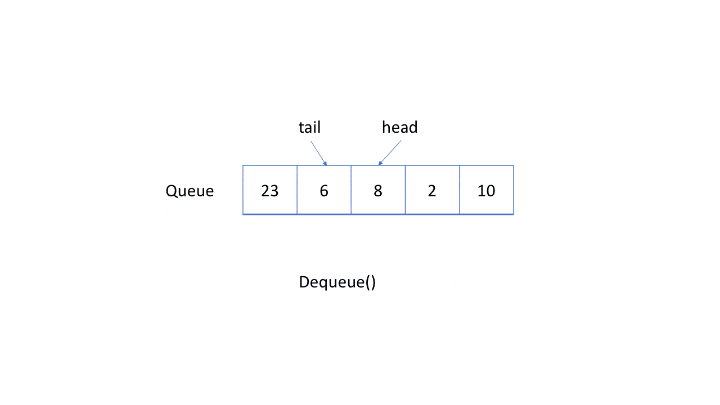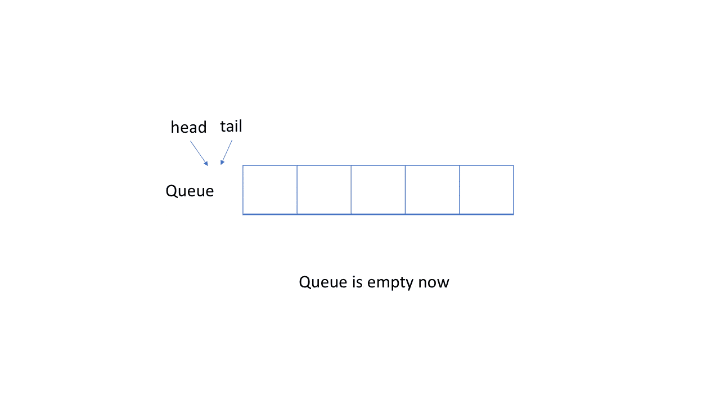
实现
按照上图演示很容易就能实现出一个版本:
class MyCircularQueue {
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k. */
MyCircularQueue(int k) {
a = new int[k];
head = -1;
tail = -1;
size = k;
}
/** Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
bool enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull()) return false;
if(isEmpty()) head = 0;
tail = (tail + 1) % size;
a[tail] = value;
return true;
}
/** Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
bool deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()) return false;
if(head == tail) {
head = tail = -1;
return true;
}
head = (head + 1) % size;
return true;
}
/** Get the front item from the queue. */
int Front() {
if(isEmpty()) return -1;
return a[head];
}
/** Get the last item from the queue. */
int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()) return -1;
return a[tail];
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not. */
bool isEmpty() {
return head == -1;
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is full or not. */
bool isFull() {
return (tail + 1) % size == head;
}
private:
int* a;
int head;
int tail;
int size;
};提交之后顺利通过了全部52个测试用例,用时32ms。虽然已经超过了99.17%的提交记录,但并不属于第一梯队。阅读第一梯队源码后发现:他们采用了一个变量来存储当前队列长度,只增加了一个变量但却大大简化了各种基本操作的判断逻辑,导致他们的代码时间性能更加良好。
于是就有了第二版:
class MyCircularQueue {
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k. */
MyCircularQueue(int k) {
size = k;
head = 0;
tail = 0;
len = 0;
a = new int[k];
}
/** Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
bool enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull()) return false;
a[tail] = value;
tail = (tail + 1) % size;
len++;
return true;
}
/** Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
bool deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()) return false;
head = (head + 1) % size;
len--;
return true;
}
/** Get the front item from the queue. */
int Front() {
if(isEmpty()) return -1;
return a[head];
}
/** Get the last item from the queue. */
int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()) return -1;
return a[(tail - 1 + size) % size];
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not. */
bool isEmpty() {
return len == 0;
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is full or not. */
bool isFull() {
return len == size;
}
private:
int *a;
int head;
int tail;
int size;
int len;
};满怀期待地提交了代码,然而用时36ms,反而比第一个版本更慢了。无奈,再次点开了第一梯队的示例代码,比对之后终于定位了问题所在:++i和i+1的时间效率不同。
- ++i:对i的值进行增一,然后返回i的值作为表达式的值。
- i++:对i的值进行增一,然后返回加一之前的i的值作为表达式的值。这就要求系统不得不开辟一个新的临时变量来存储i的值。
i=i+1:把i的值增一,然后把计算结果赋值给变量i。这里多了一个赋值操作。
我写了下面的代码来帮助理解其语义:// ++i i += 1; return i; // i++ tmp = i; i += 1; return tmp; // i = i + 1; tmp = i + 1; i = tmp; return i;以上代码仅是为了方便理解,无实际意义
于是,第三个版本就出现了:
class MyCircularQueue {
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k. */
MyCircularQueue(int k) {
a = new int[k];
head = 0;
tail = 0;
size = k;
len = 0;
}
/** Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
bool enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull()) return false;
a[tail] = value;
tail = (++tail) % size;
++len;
return true;
}
/** Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
bool deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()) return false;
head = (++head) % size;
--len;
return true;
}
/** Get the front item from the queue. */
int Front() {
if(isEmpty()) return -1;
return a[head];
}
/** Get the last item from the queue. */
int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()) return -1;
return a[(tail - 1 + size) % size];
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not. */
bool isEmpty() {
return len == 0;
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is full or not. */
bool isFull() {
return len == size;
}
private:
int* a;
int head;
int tail;
int size;
int len;
};最终用时28ms,成功跻身第一梯队,超过了100%的提交记录。